Blog
Ticks carry the decades of history in every troublesome bite
When you think about ticks, you can imagine nightmarish tiny parasites, haunting you on weekend hiking or afternoons in the park.
Your fear is justified. Diseases transmitted by a tick The most widespread disease transmitted by a vector – People passed by living organisms – in the United States. Each tick feeds on many animals throughout their lives, absorbing viruses and bacteria along the way and passing them with another bite. Some of these viruses and bacteria are harmful to people, causing diseases that can be devastating and sometimes fatal without treatment, such as LymeIN Bullshit AND Main fever of the Rocky Mountains.
But contained in every bite of this annoying, insatiable pest is also History of social, environmental and epidemiological history.
In many cases, human actions a long time ago are the reason why ticks carry these diseases so wide. And this makes the ticks fascinate Environmental historians like me.
CDC
Changing forests driven tick risk
In the 18th and 19th centuries, settlers he cleaned more than half The landed soil in the north -eastern United States, cutting out forests for wood and to make space for farms, cities and mining operations. In the case of gigantic -scale land settlement, it brought a keen decrease in wild nature. Predators such as bears and wolves were expelled, just like deer.
When agriculture moved west, the north -east began to recognize the ecological and economic value of trees, and they He returned millions of acres to the forest.
The Woods Regrew. Plant sharps, such as deer, returned, but the apical predators, which once kept their populations in check, no.
As a result deer populations wearing Borrelia BurgdorferiThe bacterium, which causes Lyme disease, grew rapidly. And he came with deer Deer ticks (Ixodes scapularis). When the glue feeds on infected deer, it can take bacteria. The tick is not hurt, but it can convey the bacteria of the next victim. In people, Lyme disease may cause fever and fatigue and If it remains untreated It can affect the nervous system.
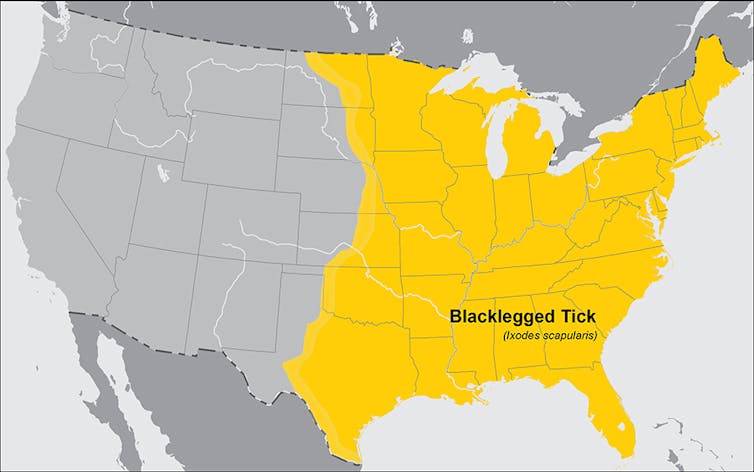
CDC
The Eastern United States has become a global scorching place for Lyme disease transmitted by a tick, starting from the seventies. Lyme disease touched over 89,000 Americans in 2023 and probably much more.
Californians move to the territory of the tick
For centuries, the changing patterns of human sediments and the policy of operate of land have shaped the role of ticks and diseases transmitted by ticks in their environment.
In brief, people have facilitated ticks to prosper and spread diseases among us.
In California, North-Seniam and the mountain ranges of Santa Cruz, which converge on San Francisco from the north and south, were never clear there, and predators such as mountain lions and coyotes. But competition for apartments PUSHED HUMAN SETTLEMENT deeper in Wild areas to the north, south and east of the citytransforming Tick ecology there.
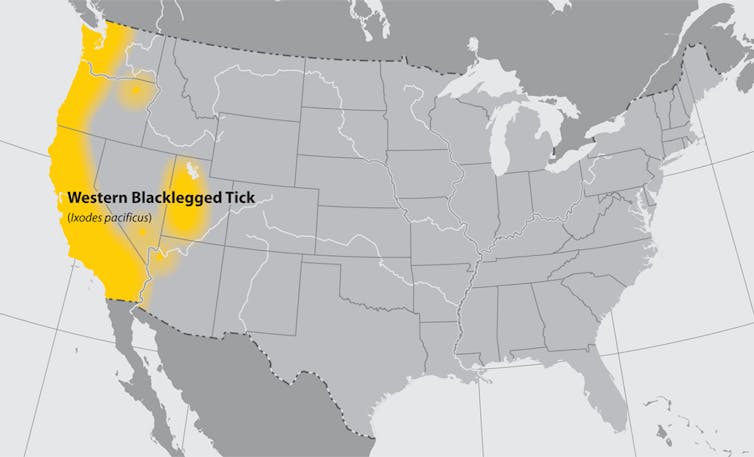
National Center
While ticks in western black legs (Ixodes pacific) tends to swarm in gigantic forest means, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease is actually more widespread in small, isolated spots of green. In these isolated rodents and other tick hosts can develop, sheltered before gigantic predators that need more habitats to move freely. But insulation and lower variety also means that infections are easier in the populations of the tick host.
People tend to build isolated houses in the hills, not gigantic, combined changes. When the Silicon Valley area south of San Francisco extends Creating a threat difficult to manage to public health.
Less hosts, more tight packed, often mean more infected hosts, proportionally and thus more perilous ticks.
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious diseases
Six poviats in these areas, all surrounding and in this San Francisco, take into account 44% of recorded diseases transmitted by ticks in California.
Lesson from Texas Ranch of cattle
Domesticated farm animals also shaped the disease threat, which is ticks.
In 1892, at a meeting of cattle ranchers at Racjer’s convention in Austin, Texas, Dr. Ba Rogers introduced a up-to-date theory that ticks are behind the recent destructive scourge of cattle fever from Texas. The disease arrived with cattle imported from Western India and Mexico in 1600, and this took Huge fees for herds of cattle. But how the disease spread to up-to-date victims was a mystery.
Nathan Banks, a treaty on Acarin or mites. Materials from the United States National Museum
Editors Daniel’s Texas Medical Journal found an idea to spread the disease Funny and annulled hypothesisPublishing the satire of what they described as a “early copy” of the upcoming report on this subject.
It is believed that “velvety secretion, there is a poison that causes a fever … [and the tick] Seeing chewing tobacco, like all other Texans, secretion is most likely tobacco juice, “they wrote.
Fortunately for the rankers, not to mention the cow, the US Department of Agriculture told Rogers. The cattle fever tick program began in 1906 Limiting where and when cattle should exceed dense areas.
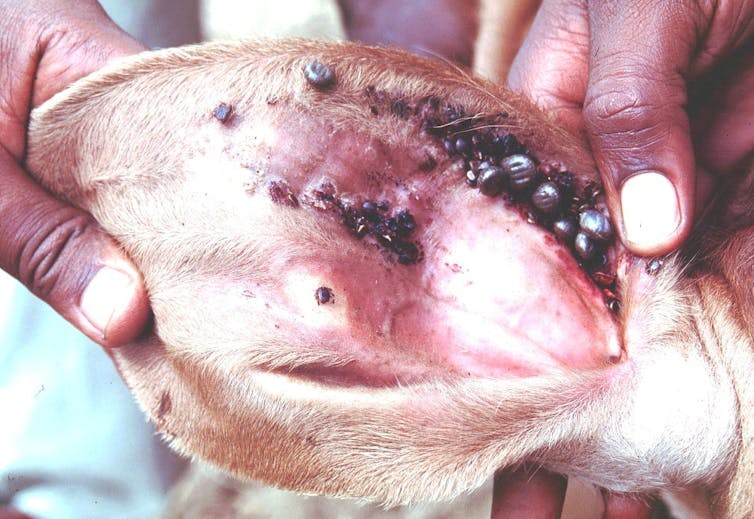
Alan R WalkerIN CC By-NC-SA
Until 1938, The government has established a quarantine zone It stretched 580 miles to 10 miles along the American-Meticus border in southern Texas, in a region preferred by a tick of cattle.
This was helped by the novel operate of natural space as a public health tool Functionally elimination Cattle fever from 14 southern states to 1943.
Ticks are products of their environment
When it comes to diseases transmitted by ticks around the world, it matters.
Take Hunter’s tick (Hyalomma SPP.) Mediterranean and Asia. As a youthful or nymph, these ticks feed on tiny forest animals, such as mice, hares and minks, but as an adult, domesticated farm animals prefer.
For centuries, Kleszcz was an occasional nuisance for nomadic shepherds in the Middle East. But in the 1850s, the Ottoman Empire passed the laws Instead, force the nomadic tribes to become settled farmers. Unsuccessful lands, especially on forested edges of the steppeSettlers were offered to create ideal conditions for Hunter ticks.
As a result, farmers nowadays Türkiye saw spikes in diseases transmitted by ticksIn this virus, which causes a criminal-congonocyte hemorrhagic fever, potentially fatal state.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ynw8x3fxjcs
There is probably too much to ask for compassion for any ticks that you will meet this summer. After all, these are blood parasites.
However, it is worth remembering that the hostility of the tick is not its own fault. Ticks are products of their environment, and people have played many roles in transforming them into harmful parasites that are looking for us today.

