Blog
What is the difference between probiotics and prebiotics? The dietitian explains
If you go through a local pharmacy or supermarket, you will certainly come across probiotics and prebiotics.
They are added to some dishes. They come as supplements that can be drunk or treated as a pill. They also occur naturally in everyday dishes.
You can have a vague idea that probiotics and prebiotics are vigorous. Or maybe you have heard that they are good for your “microbiome”.
But what is your microbiome? And what is the difference between probiotics and prebiotics?
First, some definitions
Organization of Food and Agriculture of the UN and the World Health Organization, define Probiotics as “live microorganisms, which given in the right quantities give health benefits.” These microorganisms are Bacteria and yeast in food, such as yogurt, cabbage and combustion cabbage and supplements.
But prebiotics refer to “food“Probiotics must survive and repeat.
Prebiotics are better known as dietary fiber. They include specific types of fibers called inulin fructans, galacto-olygosackahrid, resistant starch and pectin. Prebiotics occur naturally in plant food, are added to food products (such as bread and breakfast flakes) and come as supplements.
The diet fiber remains undigested in the stomach and the diminutive intestine until it reaches the vast intestine. There, microorganisms (probiotics) break down (or ferment) fiber (prebiotics), transforming them into metabolites or nutrients associated with better health.
How are they related to your microbiome?
It is said that both probiotics and prebiotics encourage Healthy microbiome. This is a vigorous community of various microorganisms that live in your body or on your body. This includes those in the mouth, intestines, skin, respiratory and urinary tract (which supports urine and has reproductive functions).
All The microbiome is different And it differs throughout his life. For example, changing your diet, physical activity, hygiene, taking antibiotics or having infection affect your microbiome.
These factors can change the diversity of your microbiome, that is, how many different types of microorganisms you have. These factors can also change the ratio of vigorous microorganisms to unhealthy.
Elif Bayraktar/Shutterstock
When your microbiome is less diverse or when the number of unhealthy microorganisms exceeds the number of vigorous, it is known as dysbiosis. This can lead to problems including diarrhea or constipation, irritable bowel syndrome, gum bleeding, atopic dermatitis (eczema) or acne.
Probiotics and prebiotics are sold as ways of supporting a vigorous, varied microbiome and lend a hand reduce the risk of dysbiosis.
Since taking antibiotics can change your microbiome, they are also sold as a way to improve the diversity of microorganisms When taking antibiotics or later.
Do probiotics work?
. The microbiome plays a key role in our health. For example, a vigorous microbiome He was associated with Reduced risk of cancer, cardiovascular diseases (heart), allergy diseases and intestinal inflammatory diseases.
But how about probiotic supplements to escalate the microbiome?
AND Review of clinical trials I looked at probiotic supplements in vigorous people. There was no escalate in the variety of their microbiome.
Other Review of clinical trials He looked at the influence of probiotic supplements when people took antibiotics. The variety of their microbiome did not improve.
Another study not contained in these two reviews showed that probiotics may worsen the variety of microorganisms in a low period. He found probiotic supplements delayed microbiome restoration After taking antibiotics.
one photo/snapshots
What about prebiotics?
Little research was carried out on the impact of vigorous people who only accept prebiotic supplements. However, there are research on people taking prebiotics with probiotics regarding specific aspects of health.
For example, one Big review He looked at various neuropsychiatric results, including dementia, Parkinson’s disease and bland cognitive disorders when people took prebiotics and probiotics (together or separately). Other review He looked at the influence of prebiotics, probiotics or synbiotics (supplements containing both prebiotics and probiotics) on people with diabetes.
But their findings are not decisive. So we need more research to routinely recommend these supplements. They are also not replaced for standard drugs and a vigorous, balanced diet.
So how do you keep my microbiome health?

Tatjana Baibakova/Shutterstock
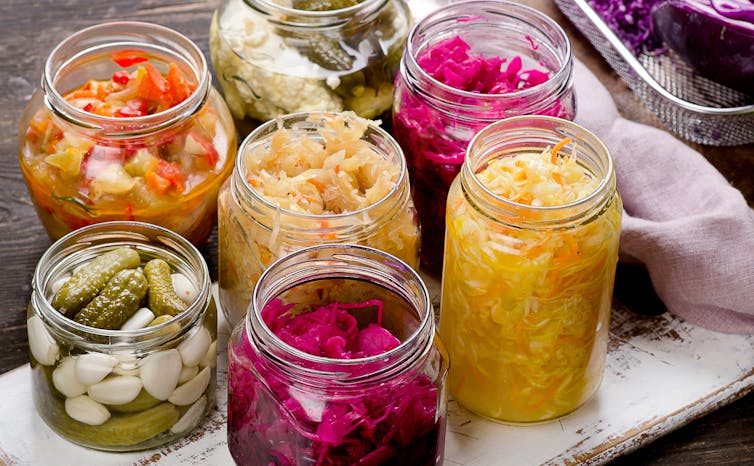
Naturally occurring probiotics and prebiotics are in daily food products.
Probiotics can be found in fermented food such as cheese, sauerkraut, yogurt, miso, tempeh and kimchi.
Prebiotics are found in food containing fiber – all plant products. It is critical to have various plant foods in your diet. This will ensure that you will receive all the types of fiber needed to maintain vigorous bacteria alive and escalate the variety of microbiome.
Food food instead of eating supplements also means that you get additional nutrients in food.
. Australian guide to healthy eating It recommends a diet luxurious in plant food and promotes eating fermented food (in the form of cheese and yogurt). This combination is ideal for maintaining a vigorous microbiome.

