Blog
What Alaska must know from Mount Spurr, which may explode
Volcany inspires the admiration of spectacular eruptions and glow of the rivers of lava, but often their most deadly threat is what quietly falls from heaven.
When a immense volcano explodes, like Mount Spurr It seems close to making about 80 miles from Anchorage in Alaska, he can spend Huge volumes of ash. Tiny ash can infilt the lungs of people and animals that inhale them, poisoned crops and disrupt water life. Broad ash deposits can collapse roofs, cripples and disturb transport networks.
Ash may not have a visual impact of flowing lava, but how A geologist who is studying disastersI know that Ash travels on, lasts longer and leaves deep scars.
Volcanic threat program, US Geological Survey
Volcanic ash: what is it and why it matters
Volcanic ash creates when sticky magma -a root-deep rock under the surface of the earth-bum, exploding into the shards of rocks, minerals and glass worn in the law of a supersonic stream of scorching gas.
High clouds of ash Height a few miles down atmosphereWhere the ash is captured by winds at high altitudes, which can be carried by hundreds or even thousands of miles.
When the volcanic ash settles to the ground accumulates in layers This usually reduces the thickness with a distance from the source of eruption. Near the ventilation, ash can have a depth of several feet, but the community can still see only vacuuming.
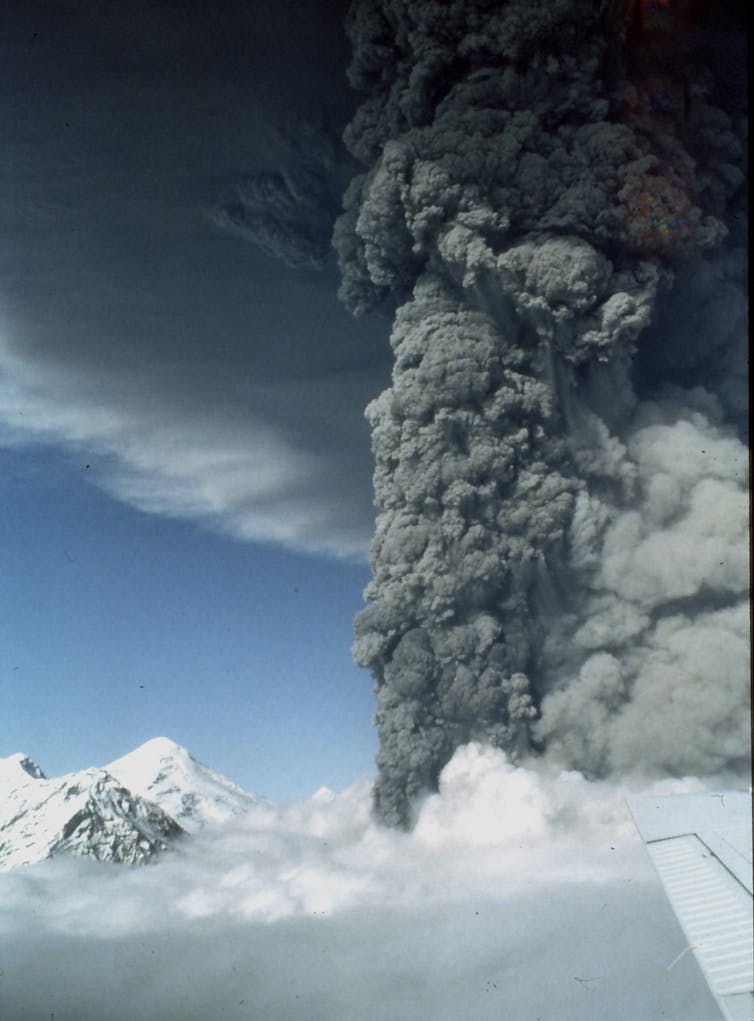

US Geological Survey
Breathing danger: health threat from ash
Breathing volcanic ash can irritate the throat and lungs, cause asthma attacks and deteriorate chronic breathing conditions such as
The best particles are the greatest risk because they can penetrate And cause death by suffocation in the worst cases. Soft, brief -term symptoms often disappear with rest. However, long -term consequences of ash exposure may include silveria, lung disease and a possible cause of cancer.
The danger increases in droughty regions, where Fallen Ash can be thrown away Again into the air through the wind or human activity.
Risk for pets and farm animals
People are not the only threatened. Animals experience similar respiratory symptoms as people.
Home Animals can develop respiratory stressEye inflammation and irritation of the paw from ash.

Federico Grosso/US geological examination
Farm animals encounters greater dangers. If Grazing animals eat volcanic ashIt can damage their teeth, block the intestines and poison them.
While Eruption eyjafjalajökull 2010 In Iceland, farmers were recommended to protect sheep and cattle because ASH contained fluorine concentrations above the recognized security threshold 400 parts per million. Animals that remained exposed, fell ill and some died.
A damage to cultivation, soil and water
Soil and crops can also be damaged. Volcanic ash changes soil acidity and introduces harmful elements such as arsenic AND sulfur to the environment.
While ash can add nutrients such as potassium and phosphorus, which raise fertility, Immediate influence is mostly harmful.
Ash maybe Marry cropBlock sunlight and clogs compact dentists or pores, in leaves that allow plants to replace gas with the atmosphere. It can also introduce toxins that make food unlimited. Vegetables, fruit trees and vines are particularly sensitive, but even solid cereals and grasses can die if the ash stays on the leaves or poisons of the appearing shoots.
After 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruptionThe wide tracts of arable fields in the central Luzon in the Philippines have become unproductive for years due to sour ash and buried soil. If there is a lot of ash during the growing season, crop failure becomes almost certain. It was The cause of historical hunger It happened Mount Tambora eruption in 1815
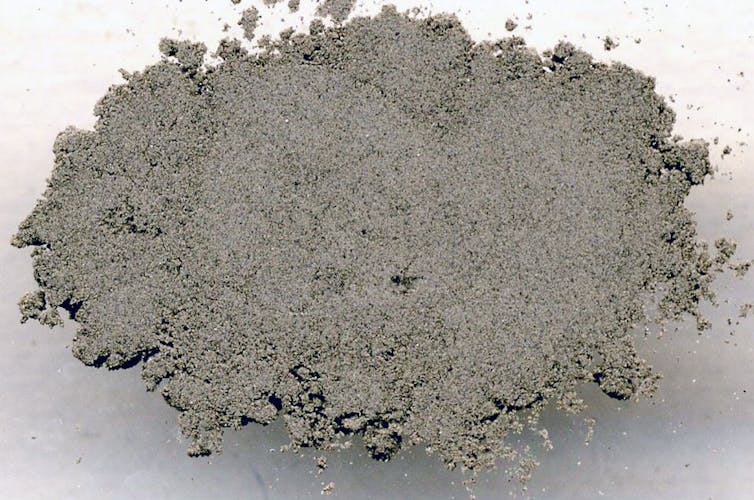

James St. John by Wikimedia CommonsIN Cc by
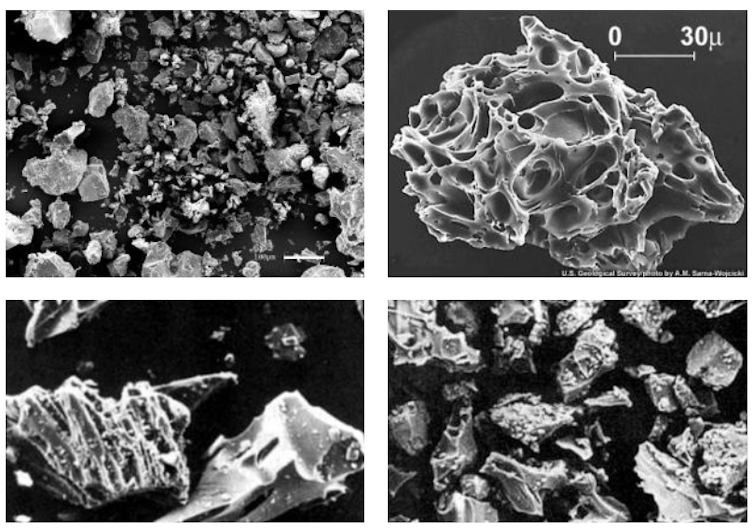
Volcanic threat program, US Geological Survey
ASH can also pollution of surface water By Introduction of toxins and increasing the acidity of water. Toxins can lean groundwater, polluting wells. Tiny ash particles can also settle in water roads and Blocked aquatic plants and animals. In 2008 Chaiten eruption In Chile, ash pollution led to universal deaths of fish in Río Blanco.
Ash maybe ground aircraft, rubber infrastructure
Ash clouds are extremely unsafe for aircraft. The glassy ash particles melt when they get into jet turbines, clog fuel systems and can get stuck in the air.
In 1982 British Airways Flight 9 Power was lost in all four engines after a flight through a cloud of ash. A similar incident took place in 1989 Flight KLM 867 over Alaska. Iceland in 2010 Eyjafjallajökull explosion grounded over 100,000 flights Throughout Europe, disturbing the journey for over 10 million passengers and costing a global economy of billions of dollars.
Volcanic ash can also Saak Havoc on infrastructure By engraving water supply, returning electrical systems and collapsing roofs under its weight. May interfere with transport, communication, rescue and energy as 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruption Dramatically demonstrated in the Philippines.
What to do during ash
During ash party, The most effective strategy Maintaining safety involves staying indoors in the room and avoiding inhalation of ash particles.
Anyone who has to go outside should wear the right N95 or P2 mask. Fabric masks provide slight protection against compact ash. Tanks, troughs and open wells should be covered and monitored for pollution. Farm animals should be transferred to tidy pastures or receive unheld feed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Woihyqrcmoe
To reduce structural damage, ash should be removed immediately from roofs and gutters, especially before rainfall.
Older adultsIN kids And people who are unwell are the most threatened, especially people living in poorly ventilated homes. Rural communities that are dependent on agriculture and farm animals are disproportionately affected by ash, like low -income people who do not have access to tidy water, protective masks or unthreatening shelter.
Communities can stay informed about the risk of ash through official alerts, including those from Volcanic ash advisory centerswhich monitor the dispersion of ash and issue timely warnings. . International network of threats to volcanic health It also offers guidelines for personal protection, emergency planning and ash cleaning.
Long tail of ash
Volcanic ash can fall quietly, but its effects are common, robust and potentially fatal. It poses a chronic threat to health, agriculture, infrastructure and water systems.
Recognition of risk is the key first step to protecting life. Effective planning and social awareness can further reduce damage.

