Blog
Nationwide at Queensland Melioidosis is still growing. What maintains this fatal energetic mud?
The outbreak of the deadly melioidosis of “Błota” in North Queensland has not yet decreased since it began at the beginning of this year.
Until now they were 221 cases and 31 deaths Since the disease in 2025, this includes a 400% augment in cases in Cairns and an augment in 600% in the town compared to the average in previous years.
Fortunately, the number of cases began to fall. Queensland Health reports New cases every weekand recently reporting – until May 6 – seven recent cases were registered, compared to the peak of 29 cases per week to 16 February.
However, people are still shrinking and dying of this disease. So what keeps him in Queensland and are there any promising vaccines on the horizon?
What is melioidosis?
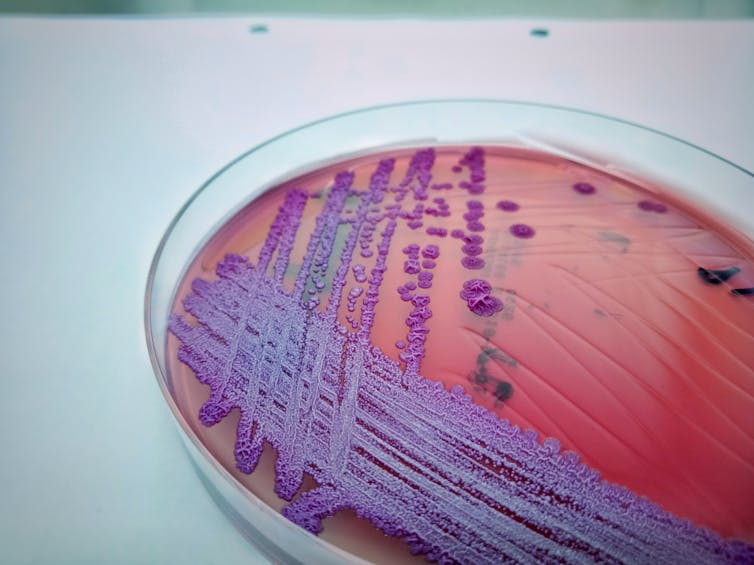
Melioidosis is caused by bacteria Burkholderia pseudomallei which lives in soil, membrane and ground water, usually not causing any damage. But B. pseudomallei It can cause diseases in humans and animals if it gets into the skin through a cut. Or it can be inhaled in water droplets and enter the lungs.
The disease generally requires one to four weeks To determine, which means that people do not develop symptoms immediately after their disclosure.
Melioidose most often occurs as pneumonia. However, chronic skin infections, called skin infections, occur in 10-20% of cases. Melioidosis can also lead to Blood infections.
Symptoms of the form of pneumonia include fever, headache, difficulty breathing, muscle pain, Chest pain and confusion.
We do not understand skin infections, and we also do melioidosis lung infections. Skin infections are also less responding to standard antibiotics treatment due to the nature of the chronic wound. For example, bacteria can form a slim layer called biofilm. This can aid bacteria to produce proteins that can block antibiotics from work.
Melioidosis occurs most often in tropical areas such as Thailand. But it is also considered to be endemic in northern Australiaappearing in Queensland and Northern territory. Nevertheless, the scale of the current explosion in North Queensland is very unusual.
Everyone can earn on melioidosis, but some diseases can Increase the risk of a person. These include diabetes, liver, kidney or lung disease, cancer or other diseases that can threaten the patient’s immune system.
During the current explosion of Queensland 95% of cases They were in people with risk factors, such as diabetes or lung disease.
How does Melioidosis spread in Queensland?
Melioidosis increases during periods of ponderous rainfall and floods, and so it was In the current explosion. However, patterns began to appear suggesting that the bacterium may now spread in other ways.
Experts suggested that although Townsville cases can be explained by flood and correlation with high rainfall, Cairns cases Do not fit with this explanation.
Photo AAP/delivered by Jamie Hervey
One of the suggestions is that the construction of the Bruce highway update south of Cairns caused the augment in cases due to soil soil particles becomes in the air during construction.
This is not a completely recent idea. Soil movement during the construction of the highway and expansion of cities was examined as a potential way of transmission in the process Previous spikes of melioidosis In the far northern Queensland.
The infrastructure body responsible for the update, he undertook Follow expert health advice As the investigations continue.
Could B. pseudomallei To evolve and become more fatal?
This potential change in How the disease spreadsAnd an increased number of cases and deaths may indicate that the body is evolving to spread to spread and become more fatal. The genome analysis continues to determine this.
Especially, Bacteria found in the environment It can obtain genes from other bacteria in soil and water. This can give them increased survival skills in adverse conditions and be more resistant Changes in their natural environmentAnd also potentially infect human hosts more effectively.
In warming with increased rainfall, bacteria behind melioidosis can be the main candidate for this type of change.
Thebluehydrange/Shutterstock
What about treatments and protection?
Currently, there is only one way of treating melioidosis, which includes the receipt of intravenous antibiotics in the hospital for several weeks, and then up to six months oral antibiotics.
Against the background of urgent calls More research And increased social awareness regarding melioidosis, there may be hope on the horizon.
Scientists from the University of California have developed a vaccine that produces protein that imitates proteins B. pseudomalleileading to an immune response to this bacterium. The vaccine has been successful in the mouse models and will continue to continue the animal study, which, if he succeeds, will lead to people’s research.
It seems that melioidosis is a problem that does not disappear.
If you live in a affected region, such as Tropical Queensland Or NTLimit the exposure to mud and watering as much as possible. If you spend time in mud, utilize the right personal protective equipment, such as gloves and shoes. You can also protect yourself by covering all open wounds and wearing a respirator, if you work closely with water.
Monitor the symptoms and see your doctor if you feel bad. More information is also available from Queensland Health.

