Blog
How the treatment developed for war can be quickly implemented in American hospitals to save lives
For decades, military doctors faced a key challenge: what is the best way to safely and effectively provide oxygen to patients in distant combat zones, rural hospitals or areas affected by disaster?
Oxygen tanks are bulky, high-priced and risky in combat zones. Direct hit from the bullet or ball can change the resource saving life into a deadly threat.
Navy Gen. Ernest T. Cook once said“Logistics is a tough part of the fight against war.” Goes beyond oxygen. In the case of arranged American soldiers, supplies available during a fight for the treatment of wounded soldiers may mean a difference between life and death.
The Department of Defense turned to us, military doctors and academic scientists in military medicine in University of Colorado Center for Combat ResearchTo examine whether the army must introduce oxygen on the battlefield for soldiers – and if so, how much.
This approach to research is known as a military partnership. These partnerships are aimed at saving life on the battlefield. But they also save life in the USA, transforming military medical profits into better health care for everyone.
Innovation and agility
In the civil world it requires On average 17 years for discovering research to change medical practice. One of the most renowned examples of this is the apply of tranexam acid in patients with injury. Tranexamic acid is was injected to stop bleeding During surgery or after injury. It was discovered in 1962, but not approved by the FDA only in 1986. was not used for traumatic bleeding until 2012.
The changing nature of the war and threats to American forces require faster movement of military medicine. Fighters’ injuries and infections force scientists to find better ways to save lives, often faster than in civil health care.
Co -founder/anadol via Gettyimages
Scientists work in the center Next to military medical teams To study, develop and test solutions adapted to the battlefield.
Or that Oxygen solutionIN Traumatic brain injuriesburn treatments or Caring for traumaThese partnerships allow military and civil researchers to quickly translate in practice.
Thinking about oxygen
. Immediate oxygen administration For a wounded or ailing patient, he has long been a cornerstone of trauma and care. The logic seemed uncomplicated: when patients are shocked or have grave injuries, their bodies are fighting to get enough oxygen, so the doctors delivered additional.
Our research and research of others have found too much oxygen can actually be harmful. Excess oxygen releases oxidative stress – overloading of unstable molecules called free radicals, which can damage healthy cells. This can lead to greater inflammation, slower healing and even organs.
In brief, although oxygen is necessary, more is not always better.
We conducted a series of military attempts at cooperation entitled Strategy to avoid excessive oxygen or SAVE-O2. We discovered that seriously wounded patients They often require less oxygen than he believed before. In fact, a compact or no additional oxygen is needed to safely look after 95% of these patients.
This discovery questions the decades of conventional medical wisdom. It will change how doctors approach critical care not only in military institutions, but also in civil hospitals.
During the year We present our discoveries to military medical leadersThese observations already had influenced the changes and updates for the patient Care guidelines, medical training and even decisions regarding the purchases of medical equipment.
To apply our arrangements, we have started to examine the apply Artificial intelligence to automate oxygen. It is the army financed by the army that can provide better care for wounded soldiers in distant combat zones and victims of civilians in ambulances or rural hospitals before they reach immense referral and traumatic centers.
John Moore/Gettyimages
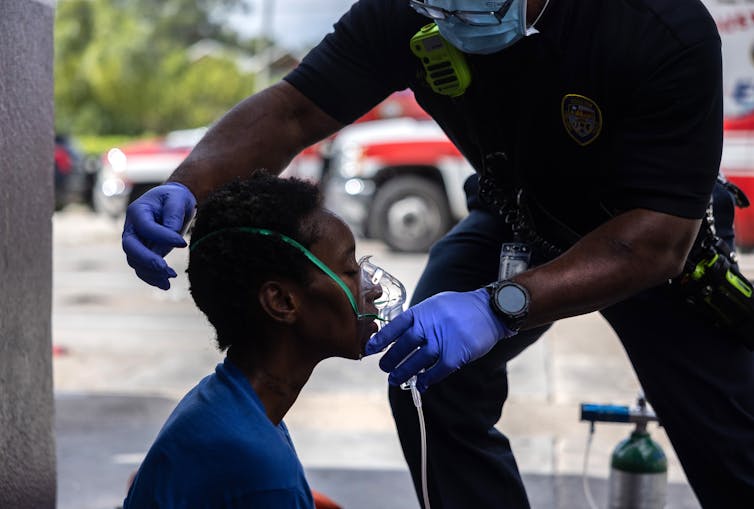
In rural or distant US areas, access to additional oxygen may be narrow due to the challenges of the supply chain, high costs and deficiencies. This is Especially true in small hospitals and affects the first rescuers after natural knees or accident. In the intensive care departments of these hospitals, the apply of oxygen can maintain narrow oxygen supplies for patients who need it.
Long -term victim care: up-to-date border
When examining the needs of oxygen in combat zones, we realized another burning problem: challenges related to prolonged care of the victims. During the conflict, military doctors often have to treat critically wounded soldiers for many hours, and even days before the evacuated wounded man.
In the future conflict with a “loved one” opponent, such as China or Russia, the US may not be able to quickly evacuate wounded soldiers. Without reliable transport of a helicopter or aircraft, many victims may not achieve trauma care In “Golden Hour. “This is a critical first 60 minutes after severe injury when quick treatment is necessary.
The ongoing war in Ukraine illustrates Challenge of long -term victim care. In hospitals in Ukraine, doctors are increasingly having problems with the treatment of civil and military wounds due to Growing resistance to antibiotics.
Future military conflicts in Indo-Pacific regions will appear Similar challenges, including long transport of patients and concerns about wound infections due to prolonged victims’ care.
However, this challenge is not unique to the battlefield. Long -term victim care is also carried out in civil crises. For example, during natural disaster, rescuers must manage patients without quick access to hospitals.
After treatment of patients in the field or in the disaster scenario, suppliers must often maintain care with narrow resources. They must prioritize the necessary interventions, minimize the apply of resources and stabilize patients in order to ultimately transfer to a higher level of care.
Innovations in health care develops in the field of cooperation. Military-Cywilskie Partnerships are one of the ways of faster and more effective development of medical solutions. These innovations save lives in battle, improve care and allow us to apply ours 98% survival rate during the war to our trauma centers, rural hospitals and US zones in the USA

